What is FTTx and how to increase business competitiveness through it?

Gabriel Vivares Arias
In the current environment of connectivity and use of the Internet is quite popular, and even the term fiber optic, or fiber optic Internet is spoken with much property, becoming almost a requirement of customers and users when requesting their Internet service, either for their homes or businesses.
This, thanks to the popularity of its benefits in terms of stability, browsing speed and access to business applications, video streaming, gaming, etc., and the flexibility to access different speeds in the order of 100, 300, 500, 500, 1Gbps (1000Mbps).
But do users and businesses really know how fiber optics reach their workplace or home, do Internet providers know its advantages and why to implement them to maximize their profitability and growth? In this article we will explain the basic concepts about FTTx, (Fiber to the x) and how it is deployed in any of the mass market scenarios, such as residential and enterprise, as well as a brief overview of the architecture and use cases or deployments most used with this technology and the GPON access network.
What is Fiber Optics?
The fiber-optics allows information to be transmitted over long distances in the form of pulses of light, using glass or plastic fiber strands that measure about the diameter of a human hair, and allow more data to be transmitted, faster and over longer distances than other media such as copper networks or radio links.
What is FTTx?
FTTx is a generic acronym, used more to designate the different connections always through optical fiber, between the provider's network and the customer's home, office or data center, including topologies or arrangements of the passive optical networks (PON: optical fiber, splitters or splitters, connectors, NAP boxes, cabinets, ODFs, etc.) that connect the Head End (central node) of the Internet Service Provider (ISP) to the users or subscribers distributed in a locality or metropolitan area.
These connections can be residential or home access (FTTH/FTTP, Fiber to The Home/Premise), corporate or installed to the local/home/building end (FTTB, Fiber To The Building) and fiber laid to the cabinet/node, with copper wires to complete the connection (FTTC / N, Fiber to the Curb /Node).
In more precise terms, FTTx is the deployment of the fiber optic network (cables and other components) to a specific location or area, in reference to the customer premises, using the "x" to describe the application or use case of the service.
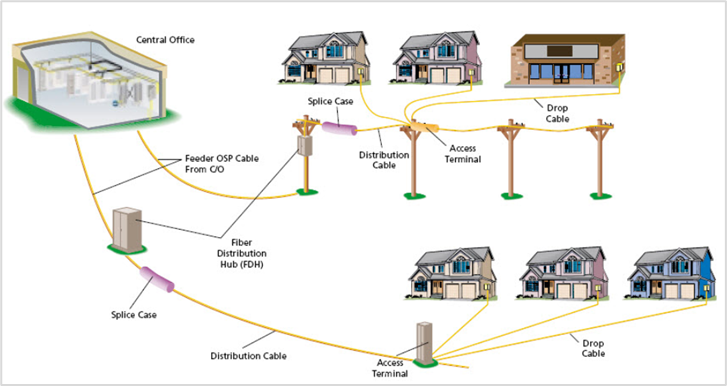
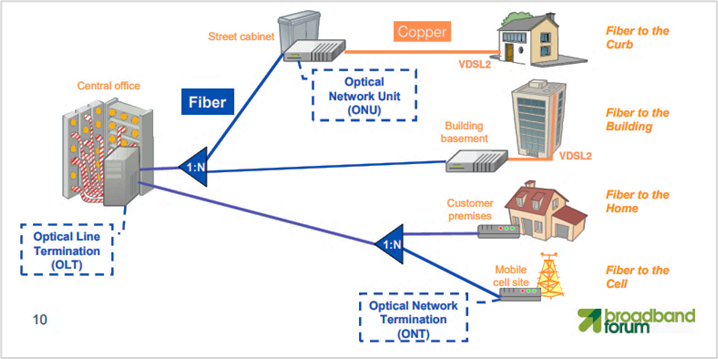
Figure 1 illustrates the different architectures or deployment models of FTTx as an access network infrastructure.
Figure 1 illustrates the different architectures or deployment models of FTTx as an access network infrastructure.
In Figure 1, the passive network includes from the ODF at the Head End or Central Office, the outside plant fiber cables (feeder cable, distribution and drop), the splitters or stage1 and stage2 splitters, to the Street cabinet or NAP boxes inside buildings.
There are many variants of FTTX such as FTTO (Fiber To The Office), FTTN (Fiber To The Node), FTTA (Fiber To The Antenna), FTTM (Fiber To The Mobility Base Station or Cell), FTTD (Fiber To The Door), but whose ultimate goal is to reach the customer's premises to deliver a broadband fiber optic service.
Figure 1a: General Architecture http://www.broadbandsoho.com/FTTx_Tutorial.htm
..
Figure 1b: FTTx architecture for GPON
https://www.broadband-forum.org/download/MR-246.pdf
Figure 1. FTTx deployment models. a)General Architecture and b) FTTx Architecture for GPON
What are the advantages of FTTx?
.
FTTx technologies facilitate mass market Broad Band access (Broad Band), both business and corporate and residential, which allow aggregating high capacity traffic and optimizing the use of the fiber optic network to improve efficiency in the provision of services to the end user, such as Internet, Carrier Ethernet, content delivery such as Video Streaming, Gaming, IP Voice or IP telephony, among others.
The implementation costs might be higher at the beginning, but the advantages and reduction of CAPEX (investments) and OPEX (operating expenses) that follow after implementation justify the initial investment.
Thus, FTTx enables high scalability for future expansion, with excellent quality of service and efficient use of fiber optic infrastructure resources.
FFTx technologies allow service providers to offer increasingly common bandwidths such as 100 Mbps that other technologies do not support.
They also allow the bundling of services such as: Internet, Television, Telephony, connection between sites over a single path to the customer's premises.
Our commitment is to support ISPs in your growth and transformation, access here to a site created with exclusive content for this industry.
Frequently Asked Questions about FTT
What are the advantages of deploying FTTx networks compared to other Internet connection technologies?
The deployment of FTTx networks offers several significant advantages. First, it provides much higher connection speeds compared to technologies such as ADSL or coaxial cable. In addition, optical fiber has a greater capacity to handle large volumes of data and support high-quality multimedia services.
What are the main considerations in designing an FTTx network?
When designing an FTTx network, it is essential to consider the required coverage and the density of users in the deployment area. In addition, deployment costs must be evaluated, including laying the fiber optic and installing the necessary equipment.
What are the common challenges in deploying FTTx networks?
One of the common challenges in deploying FTTx networks is the cost associated with deploying the fiber optic infrastructure. In addition, managing and maintaining an FTTx network requires specialized skills and specific tools. Another challenge is coordination with authorities and proper planning of the existing subway and overhead infrastructure.





.jpeg?width=352&name=technology%20company%20(1).jpeg)
.jpeg?width=352&name=FTTX%20(1).jpeg)





.jpeg?width=352&name=Cliente%20(1).jpeg)